Re-define AI Processing.
Built on Computing In-Memory & RISC-V Architectures.
Computing In-Memory
Computing In-Memory (CIM) is an innovative approach that integrates computational processes directly within memory units, reducing data transfer delays compared to traditional accelerators. By embedding ALUs (Arithmetic Logic Units) in memory banks, CIM minimizes reliance on the databus, enhancing efficiency and speed for data-intensive tasks.
Traditional Accelerators
Computing In-Memory
Analog Computing
Analog Computing leverages continuous signal processing to perform computations, using components like DACs (Digital-to-Analog Converters) and ADCs (Analog-to-Digital Converters) to handle complex calculations. This method, integrated with modern CPU and memory systems, offers high parallelism and energy efficiency, making it ideal for specialized applications.
RISC-V Architecture
RISC-V is an open-source, license-free CPU architecture that offers a modular design, making it highly adaptable for various applications. Its open nature fosters innovation, while its modularity benefits edge AI by enabling efficient, customizable processing tailored to specific needs, reducing costs and enhancing performance in resource-constrained environments.
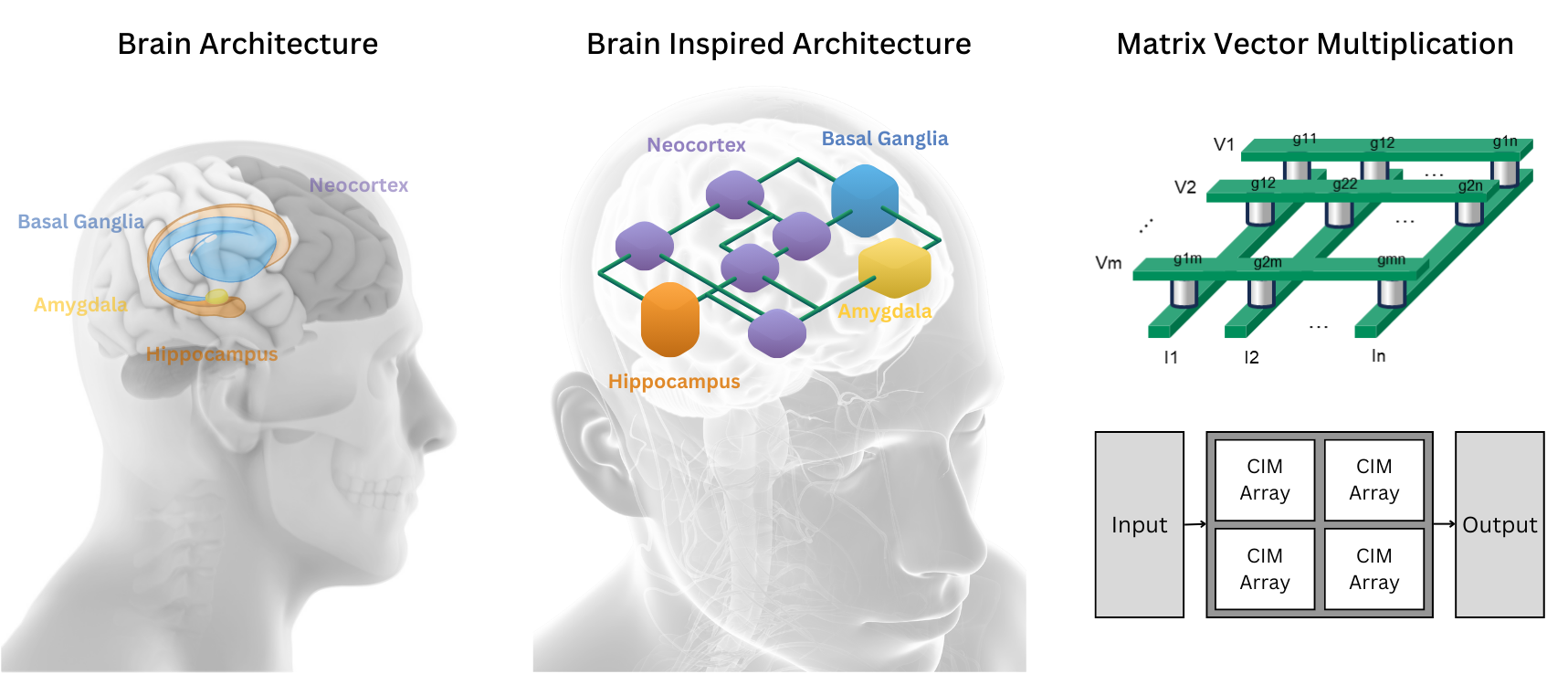
Neuromorphic Computing
Drawing inspiration from nature's most sophisticated computer, the human brain, we employ an analog computing architecture integrated with Analog In-Memory Computing & RISC-V. Due to its physical properties, analog computing operates in a manner similar to the brain, processing information through continuous signals which allows for natural efficiency and parallelism.